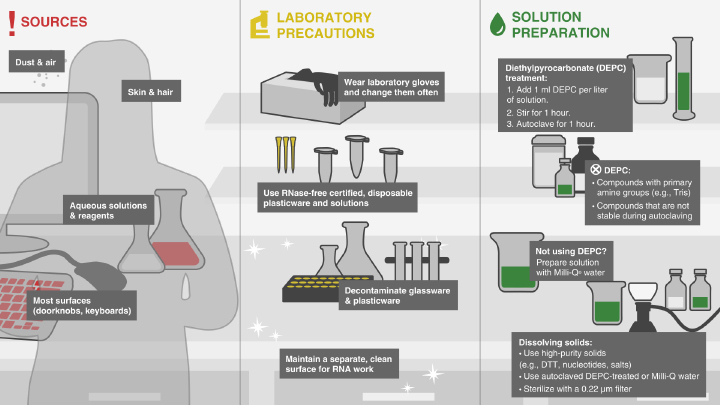
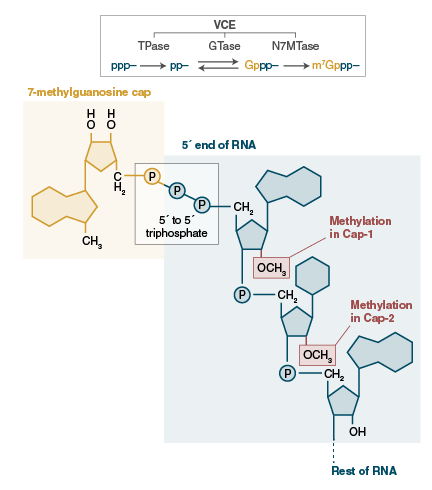
Sign In or Sign UpMy NEB
NEBinspired Blog
Afrigen's Mission to Empower Developing Countries with mRNA Vaccine Production. 15-11-2024
Press Release
Just updated. Check out our special offers page. Valid from Oct 1 to Dec 31, 2024. 08-10-2024
- NEB Products
- CST Products
Product Categories
- Active Kinases
- Adhesion
- Alexa Fluor Conjugated Antibodies
- Angiogenesis
- Antibody Sampler Kits
- Apoptosis
- Assays and Reagents
- Autophagy Signaling
- Ca, cAMP & Lipid Signaling
- CD Markers
- Cell Cycle / Checkpoint Control
- Chromatin IP
- Chromatin Regulation / Acetylation
- Companion Products
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- DNA Damage
- FastScan™ Sandwich ELISA Kits
- Flow Cytometry
- General Phospho-Ser/Thr/Tyr Antibodies
- Glucose / Energy Metabolism
- Growth factors/cytokines
- Immunofluorescence
- Immunohistochemistry
- Innate Immunity
- Jak/Stat Pathway
- Lineage Markers
- Lymphocyte Signaling
- MAP Kinase Signaling
- Neuroscience
- NF-kappaB Signaling
- Nuclear Receptor Signaling
- PathScan Sandwich ELISA Kits
- Phosphatases
- PI3K / Akt Signaling
- Protein Folding
- Protein Stability
- Protein Translation
- Rabbit Monoclonal Antibodies
- Screening Technologies
- SignalSilence siRNA
- SignalStar™ Multiplex IHC
- Stem Cell Markers
- Tag Antibodies
- TGF-beta/Smad Signaling
- Transcription Factors
- Translational Research
- Tyrosine Kinases / Adaptors
- Vesicle Trafficking
- Wnt / Hedgehog / Notch
- Quick Buy
- Freezer Program
- Tools & Resources
- Support
- Samples & Offers
- About