The Q5 High GC Enhancer is an additive that should be used when dealing with particularly difficult or high GC templates, but can be inhibitory when using high AT content templates.
The stand-alone Q5 enzyme can cover a wider range of GC content (up to 80%) with the addition of the GC enhancer.
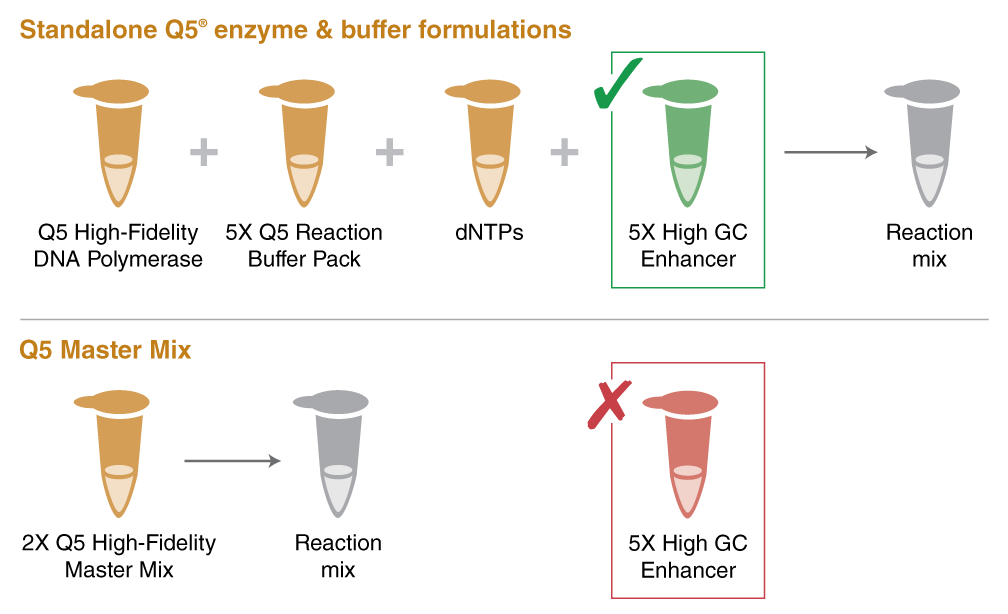
Q5 High GC Enhancer is a supplemental reagent to Q5 enzyme and buffer formulations (M0491 and M0493) and should not be used alone.
*This Enhancer is not a stand-alone buffer and should not be used on its own. Additionally, it should not be added to any Q5 Master Mixes (M0492, M0494, M0500, E0555).
Q5U does not benefit from the Q5 High GC Enhancer and we do not recommend using it. The addition of common PCR additives, such as up to 2% DMSO, may improve amplification of certain difficult or long targets.
It is often not necessary to alter the annealing temperature of your reaction after adding Q5 High GC Enhancer. We recommend using our Tm calculator to determine the annealing temperature of your PCR.
Learn More
Use of the Q5 High GC Enhancer often lowers the effective range of temperatures at which specific amplification can be observed by reducing complex template secondary structures, which can increase the amplification of your target DNA and improve your yield of hard to amplify products, such as GC rich templates.
Generally, PCR additives usually work one of two ways:
- By reducing secondary DNA structures, thus increasing the amplification of your target DNA
- Secondary DNA structures can be destabilized by additives that bind to the minor and major grooves of DNA and affecting hydrogen bonding of the duplex.
- Secondary structures include the double helix (increased hydrogen bonding due to increased GC content) and stem-loop structures (hairpins or bulging nucleotides that reduce hybridization)
- Secondary DNA structures can be destabilized by additives that bind to the minor and major grooves of DNA and affecting hydrogen bonding of the duplex.
- By reducing non-specific priming and thus reducing the amplification of off-target DNA.
