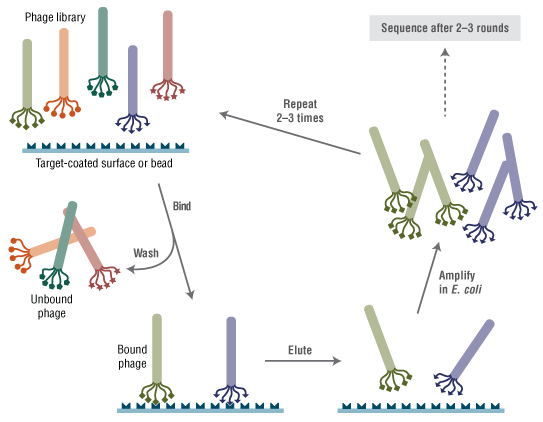
The Ph.D.™-C7C Phage Display Peptide Library Kit contains a tube of the Ph.D.-C7C Phage Library, protein reagents for a control reaction and sequencing primer stocks. The Ph.D.-C7C library is a combinatorial library of random peptides with a disulfide constrained loop, fused to a minor coat protein (pIII) of M13 phage. The displayed peptide, in the form AC-X7-CGGGS, is expressed at the N-terminus of pIII. The library consists of approximately 1 x 109 electroporated (i.e., unique) sequences.
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.
New England Biolabs (NEB) is committed to practicing ethical science – we believe it is our job as researchers to ask the important questions that when answered will help preserve our quality of life and the world that we live in. However, this research should always be done in safe and ethical manner. Learn more.