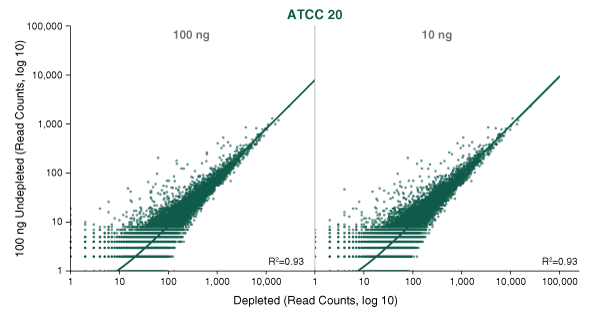
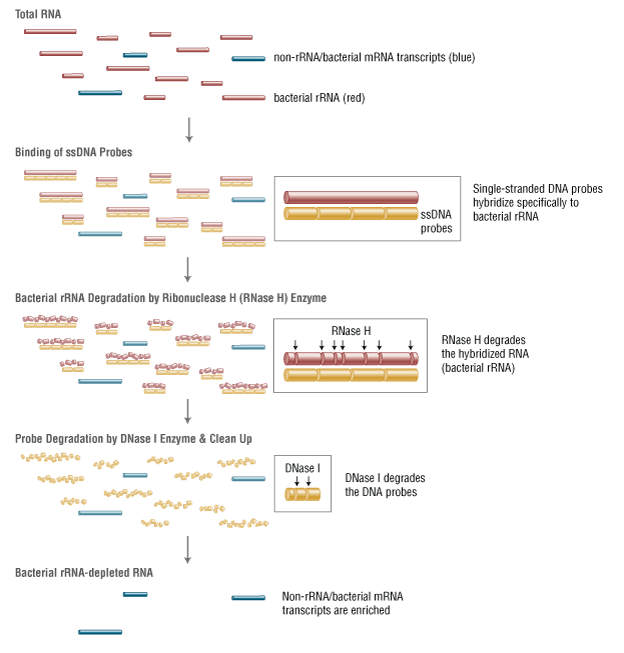
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is highly abundant in bacterial samples, and its removal is desirable in order to reveal the biological significance of less abundant transcripts. Specific enrichment of bacterial mRNAs is challenging due to their lack of poly(A) tails, and so the converse - efficient and specific removal of bacterial rRNA – is necessary.
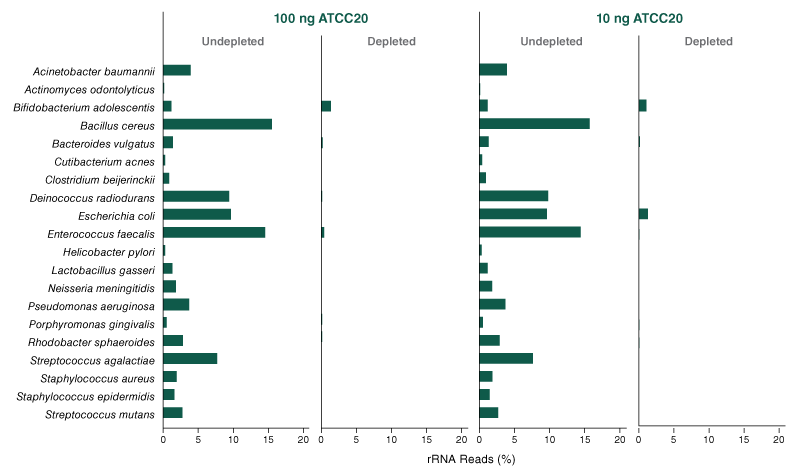
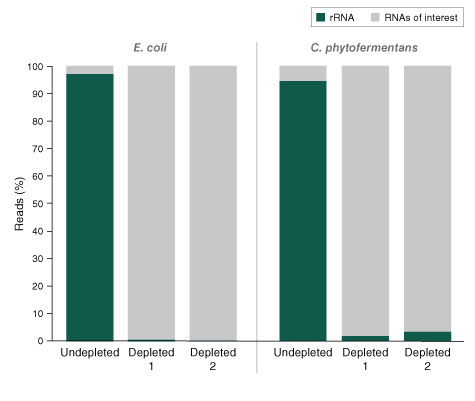
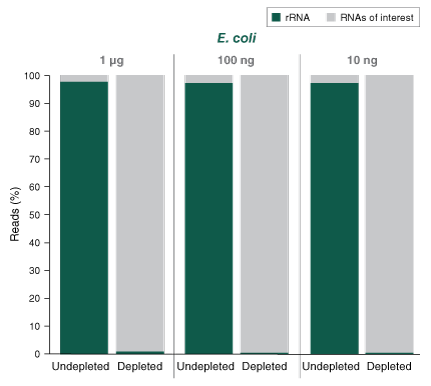
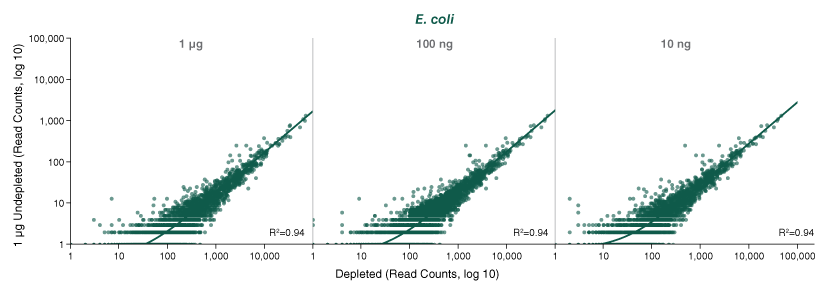
The NEBNext® rRNA Depletion Kit (Bacteria) employs the NEBNext RNase H-based RNA depletion workflow to target removal of rRNA from gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. The method is effective with intact and degraded RNA, from monocultures or samples with mixed bacterial species (e.g., metatranscriptomic).
The kit is also available with RNAClean® beads.
The great majority of RNA in bacteria is ribosomal RNA (rRNA). This highly abundant RNA can conceal the biological significance of less abundant transcripts, and so its efficient and specific removal is desirable.
The NEBNext® rRNA Depletion Kit (Bacteria) employs the NEBNext RNase H-based RNA depletion workflow to deplete rRNA (5S, 16S, and 23S) from gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. View species tested to date.
The kit is effective with both intact and degraded RNA preparations, from monocultures or samples with mixed bacterial species (e.g., metatranscriptomic).
The kit is also available with RNAClean® beads.
Features
The following reagents are supplied with this product:
| NEB # | Component Name | Component # | Stored at (°C) | Amount | Concentration |
| E7850S | -20 |
| NEBNext® DNase I | E7753-2VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.015 ml | 20,000 units/ml | |
| NEBNext® Thermostable RNase H | E7752-2VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.012 ml | 5,000 units/ml | |
| NEBNext® Bacterial rRNA Depletion Solution | E7851-2VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.012 ml | ||
| RNase H Reaction Buffer | E6312-2VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.012 ml | ||
| DNase I Reaction Buffer | E6315-2VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.03 ml | ||
| Nuclease-free Water | E6317-2VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.4 ml | ||
| NEBNext Probe Hybridization Buffer | E6314-2VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.012 ml |
| E7850L | -20 |
| NEBNext® DNase I | E7753-3VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.06 ml | 20,000 units/ml | |
| NEBNext® Thermostable RNase H | E7752-3VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.048 ml | 5,000 units/ml | |
| NEBNext® Bacterial rRNA Depletion Solution | E7851-3VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.048 ml | ||
| RNase H Reaction Buffer | E6312-3VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.048 ml | ||
| DNase I Reaction Buffer | E6315-3VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.12 ml | ||
| Nuclease-free Water | E6317-3VIAL | -20 | 1 x 1.5 ml | ||
| NEBNext Probe Hybridization Buffer | E6314-3VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.048 ml |
| E7850X | -20 |
| NEBNext® DNase I | E7753-4VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.24 ml | 20,000 units/ml | |
| NEBNext® Thermostable RNase H | E7752-4VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.192 ml | 5,000 units/ml | |
| NEBNext® Bacterial rRNA Depletion Solution | E7851-4VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.192 ml | ||
| RNase H Reaction Buffer | E6312-4VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.192 ml | ||
| DNase I Reaction Buffer | E6315-4VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.48 ml | ||
| Nuclease-free Water | E6317-4VIAL | -20 | 1 x 6 ml | ||
| NEBNext Probe Hybridization Buffer | E6314-4VIAL | -20 | 1 x 0.192 ml |
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.
New England Biolabs (NEB) is committed to practicing ethical science – we believe it is our job as researchers to ask the important questions that when answered will help preserve our quality of life and the world that we live in. However, this research should always be done in safe and ethical manner. Learn more.